

This policy brief is based on Bank of Italy, Occasional Papers Number 945. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the institutions the authors are affiliated with.
Abstract
Europe’s ability to navigate the green and digital transitions hinges on its innovation capacity. Patent data from the European Patent Office (EPO) and the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) reveal a continent with robust yet uneven technological capabilities. While Germany and France lead in patent volume and quality, regional and institutional asymmetries persist, particularly in the Southern countries A deeper understanding of where and how innovation happens—and why it doesn’t—offers actionable insights for shaping an inclusive European innovation agenda. This note draws on recent evidence to map Europe’s evolving patent landscape and proposes targeted policy levers to support strategic innovation hubs and unlock underutilized potential.
As Europe pursues its green and digital transitions, the distribution of innovation capabilities has become a central concern. Recent data show that while the continent hosts several world-class innovation ecosystems, the aggregate European performance masks persistent divides—between North and South, urban and rural, incumbents and new entrants. Meanwhile, China has rapidly overtaken the EU, US, and Japan in international patent filings in strategic sectors such as AI, highlighting the urgency for Europe to reinforce its innovation leadership.
The challenge is not just to boost the number of innovations, but to ensure their diffusion across regions and sectors. Place-based innovation strategies are essential to balance scale with inclusivity and to align technological potential with the goals of EU industrial and climate policy.
PCT patent data confirm a striking shift in the global innovation frontier. Since 2008, China has surpassed Europe and the US in both AI and green tech patent filings, a sign of growing international relevance and ambition. Europe retains strongholds in environmental technologies and digital manufacturing but is increasingly challenged in AI and platform-based innovation.
In this context, Europe’s competitive advantage will hinge on its ability to combine regulatory leadership (e.g., through the AI Act and Green Deal) with policies that activate innovation ecosystems across all Member States—not just the traditional leaders.
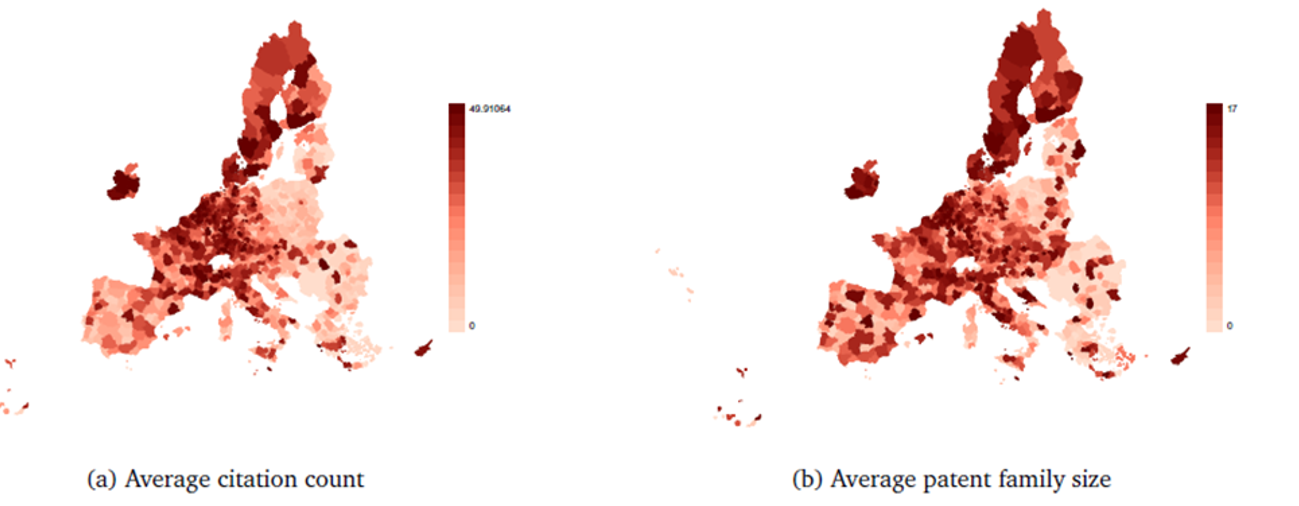
Within the EU, innovation remains geographically concentrated. EPO patent data show that Central and Southern Germany, the Paris region, the Benelux, and Northern Italy dominate the patenting landscape. However, a different picture emerges when examining quality: regions in Sweden, Finland, and the Netherlands outperform in both average patent citations and international family size—proxies for technological relevance and global reach.
Southern and Eastern European regions continue to lag in both dimensions. Yet Italy offers an instructive case: while total patenting is lower, the share of green patents is comparatively high, and regional hubs in the North and Center (e.g., Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, Lazio) exhibit strong specialization.
Figure 1. Cumulative stocks of patent applications across Europe
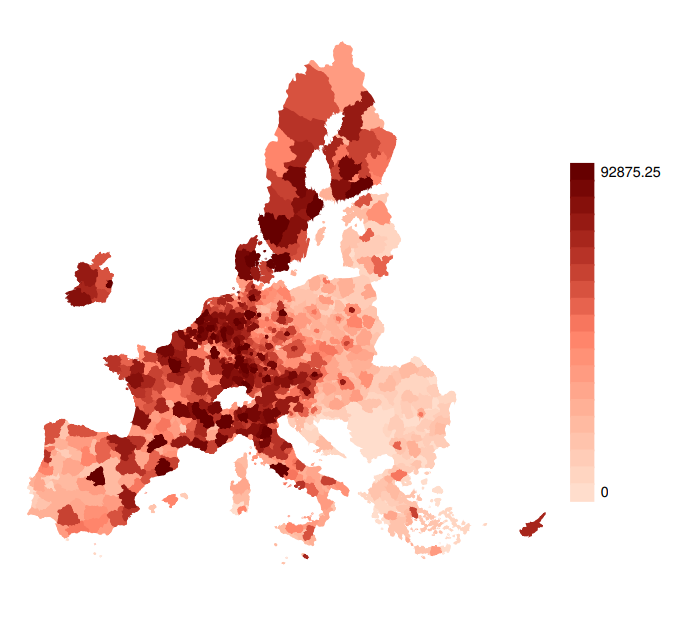
Figure 2. Average patent quality within European regions
Across Europe, AI innovation is more concentrated and firm-led, with France and Germany leading. Italy and Spain lag in both volume and intensity. Conversely, green innovation is more broadly distributed. Italy stands out for its relative specialization in transport-related mitigation technologies and its higher share of green patents within total filings—although this share has stagnated since the global financial crisis.
At the regional level, AI patenting is largely confined to industrial northern hubs, while green innovation shows greater diffusion, including into parts of Southern Italy. This divergence suggests green tech may serve as an entry point for widening the innovation base.
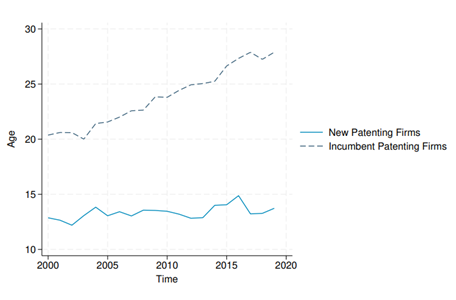
Patent data across Europe indicate that innovation is increasingly driven by older, larger, incumbent firms1. In countries like Italy, the share of new and “one-shot” patenting firms is in steady decline, while the average age of first-time innovators now exceeds 14 years. This pattern is troubling for several reasons:
In short, when innovation becomes concentrated among a shrinking pool of older firms, it not only reduces diversity of ideas but weakens creative destruction, i.e. the mechanisms that translate technology into broad-based growth. The EU’s long-run competitiveness and strategic autonomy may be at stake.
Figure 3. Average age of patenting firms at entry into innovation
While firms dominate the European patent landscape, public institutions and universities remain marginal players—especially outside France and Spain. In Italy, public research institutions account for less than 10% of AI and green patent filings, and activity is often localized to large urban centers.
Increasing the public sector’s innovation footprint—through mission-driven research programs, stronger university-industry links, and reforms to public procurement—could help diversify innovation sources and catalyze broader participation in the Twin Transition.
To reinforce Europe’s innovation capacity and strategic autonomy, policymakers should act on many fronts:
Europe’s innovation landscape is both rich and fragmented. To maintain its relevance in an increasingly contested global economy, the EU must move beyond aggregate R&D targets and embrace a place-based, inclusive innovation strategy. The patent data reveal not just where innovation is happening, but where it could—and should—emerge. Leveraging this knowledge is essential to ensure that Europe remains not just a regulator of technology, but a global leader in creating it.
European Commission (2024), Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU (SRIP) 2024 Report.