

This Policy Brief is based on the publication “Stablecoins – DeFi, Libra and beyond” by Heike Mai, Deutsche Bank Research, March 2022.)
Stablecoins are still a small segment of the crypto market but have grown robustly, recent turmoil notwithstanding. Today, they are mostly used for trading, lending and borrowing crypto assets in decentralized finance (DeFi). In the future, stablecoins could also gain traction in the real world – adding to competition in the fields of retail and corporate payments. Stablecoins differ considerably in their price stabilization mechanisms and can pose risks, which have come into the spotlight of regulators.
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies with a stable price in fiat currency – most of them are pegged 1:1 to the USD. Albeit a small segment of the crypto universe, their market capitalization has increased multifold since the beginning of 2021, even though the “traditional” crypto market has lost over half of its value since November (May: USD 1.3 tr). Also, most stablecoins withstood the turmoil when Terra USD crashed in May, leaving the market with a capitalization of USD 160 bn. But most importantly, stablecoins are the most traded coins in the entire crypto space. Tether, the leading stablecoin, represents only about 6% of the value of the entire cryptocurrency market. But Tether’s share in cryptocurrency trading fluctuates around an impressive 50%. Thus, it surpasses even the “top dogs”, Bitcoin and Ether.
Figure 1: Distribution of crypto market capitalization, May 2022
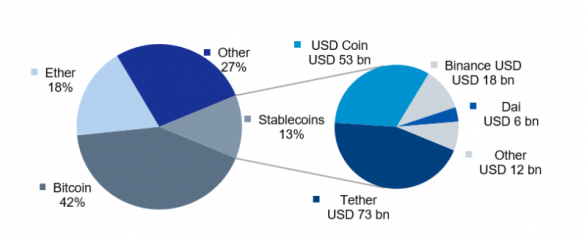
Sources: CoinGecko, Deutsche Bank Research
Stablecoins are now mostly used for trading, lending and borrowing crypto assets. They are a crucial facilitator of decentralized finance (DeFi) – financial services performed by applications on a permissionless blockchain. DeFi has been thriving on the back of innovation and speculative capital attracted by the prospect of higher returns than in traditional (“centralized”) markets. Total value locked (TVL) – i.e., the value of crypto assets placed in DeFi applications as collateral or liquidity – grew from USD 30 bn to USD 234 bn during 20211. Stablecoins are commonly used for trading crypto assets on and between exchanges, offering fast and efficient transactions without requiring users to convert their assets into fiat currencies or to use bank wire transfers during the process. Holders can earn income by depositing stablecoins, just like other cryptocurrencies, in liquidity pools which provide the funds needed for decentralized trading or lending platforms. Of course, this does not go without the risk of loss2. Stablecoins are essential for the functioning of DeFi, as they provide an anchor of stability and means of payment built on distributed ledger technology. At the same time, stablecoin use flourishes with DeFi expansion.
Figure 2: Stablecoin market cap
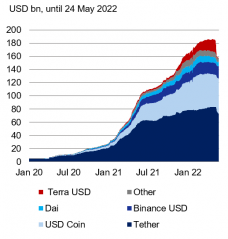
Sources: CoinGecko, Deutsche Bank Research
Stablecoins first became widely known as a potential means of global retail payments when Meta (then Facebook) announced its Libra project in 20193. While this far-reaching plan did not gain the anticipated traction, there are numerous other projects with more limited and step-by-step approaches targeting retail and corporate needs. PayPal confirmed it is working on a proprietary stablecoin for payment purposes, cooperating with financial authorities from the very beginning4. Meta is piloting payments via WhatsApp and the Novi wallet, which was originally created for Libra but now holds USD Paxos stablecoins5.
Contrary to traditional crypto assets, which typically entail sizeable price volatility, stablecoins are tokens that aim to minimize price fluctuations by pegging their value to another asset or pool of assets. They use collateral and/or employ market-based strategies to keep their price stable relative to the reference asset. Revenue for stablecoin issuers may come from different sources. Depending on the design, income can include interest earned on the reserve assets (usually not paid out to coin holders) and fees for transactions, issuance and redemption. More novel revenue sources are secondary tokens, which can be issued in addition to the actual coin for special functions within the arrangement. They are designed to generate income for the issuer6.
While there are many different approaches to classifying stablecoins, a fairly obvious one is to look at their collateralization and price-stabilization mechanisms7. Following this approach, stablecoins can roughly be split into three groups: i) Off-chain collateralized, ii) on-chain collateralized, and iii) uncollateralized, purely algorithmic stablecoins.
Operational risks specific to stablecoins arise from the difficulty of combining high levels of safety and efficiency on permissionless blockchains. Weak technical setups can increase the risk of compromised ledgers and cyber-theft. A lack of regulatory oversight gives rise to concerns about market integrity. There is little transparency about stablecoins’ setup and financial transactions, especially for those who cannot read code. This opens the door for potential abusive market behaviour, theft and illegal payment flows. However, stablecoin volumes are too low to be abused at large scale for circumventing sanctions, a concern raised with regard to Western sanctions, which were imposed in response to Russia’s attack on Ukraine10.
Off-chain stablecoins in particular can be prone to fraud, as holders are in a weak position to check if the issuance is fully collateralized as promised. Issuers could be tempted to cover their outstanding coins only fractionally or to lend reserve assets on – practices seen before in nascent and unregulated markets throughout monetary history. In October 2021, market leader Tether was fined by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) because it had misrepresented its reserves11. Asset-backed coins are subject to run risk and could spread financial distress via asset markets to traditional finance, depending on the stablecoins’ scale. Indeed, stablecoins backed by traditional fiat assets may not be so different from MMFs, as their reserves are quite similar (short-term debt).
Though spillover risks from stablecoins to the broader financial system are currently limited, they could quickly become reality. Therefore, international and national standard-setting bodies largely agree that prudential regulation will be necessary.
In the EU, the Regulation on Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) (which is supposed to be finalised by end-2022) will be the regulatory basis for stablecoin arrangements and other crypto assets. Stablecoins will probably be classified as (i) e-money tokens (backed by a single fiat currency) subject to the existing E-Money Directive unless otherwise specified or as (ii) asset-referenced tokens (ARTs, referencing a basket of assets). The latter will be subject to standards regarding the reserve assets, as well as regarding own funds, governance, disclosure and consumer protection. MiCA will prohibit all stablecoin issuers from paying interest to users and will require any arrangement, including existing ones, to obtain authorization before commencing operations. In addition, “significant stablecoins” will have to meet higher requirements as regards liquidity management, interoperability and own funds12.
In the US, the top government and oversight authorities (Treasury, Federal Reserve, SEC, CFTC, FDIC and OCC) jointly recommended in a Report on Stablecoins in November 2021 that Congress act promptly to regulate stablecoins. The agencies urged legislators to require stablecoin issuers to be insured depository institutions, to guard against run risks, and to comply with measures limiting systemic risk13. After the recent crash of Terra USD, the pressure on Congress to act has been mounting. Many officials are calling for prudential regulation of stablecoins and a clear assignment of supervisory powers.
Although currently a niche financial instrument, stablecoins might become established as a means of payment and store of value outside of the crypto market. Future regulation and the potential involvement of BigTechs or payments companies could make stablecoins an option for retail payments and support quick adoption by many users. Corporate demand could also become a driver for stablecoin adoption. As firms are increasingly interested in distributed ledger technology to underpin their internal processes, they will be looking for DLT-based financial services for seamless integration and as an enabler of new technical solutions like programmable payments. DeFi, the growth driver so far, will be tested with more restrictive monetary policies ahead. In the longer term, robust DeFi services could still become mainstream.
To sum it up, stablecoins can cater for DLT payment needs outside the hitherto parallel world of crypto assets but will face competition. So far, stablecoins are used only in the crypto space, and they carry a number of risks. Other options like tokenized bank deposits14 or digital currencies issued by central banks15 are mostly at conceptual or test stages, but first projects have gone live. Moreover, efficient traditional payment systems will rival blockchain-based solutions. Regulatory authorities will probably act if stablecoin volumes become significant, to enhance the stability of the financial system – be it traditional, crypto or merged – as well as the means and mechanisms of exchange it is built on.
CoinGecko (2022). Yearly Report 2021.
Adachi et al. (2021). The expanding functions and uses of stablecoins, in: ECB, Financial Stability Review, November.
Mai, Heike (2019). Libra – a global challenger in payments and for central banks? EU Monitor, Deutsche Bank Research, July 22.
Bloomberg (2022), PayPal Explores Launch of Own Stablecoin in Crypto Push, January 7.
PYMNTS.com (2021). Is Paxos the New Diem? The Stablecoin Issuer’s Facebook Pilot Just Expanded to 2B WhatsApp Customers, December 10.
Lipton et al. (2020). From Tether to Libra: Stablecoins, Digital Currency and the Future of Money, papers 2005.12949, arXiv.org.
Berentsen, Aleksander, and Fabian Schär (2019). Stablecoins: The quest for a low volatility cryptocurrency, in: VoxEU, The Economics of Fintech and Digital Currencies.
Lyons, Richard K., and Ganesh Viswanath-Natraj (2020). What keeps stablecoins stable?, NBER, Working Paper Series, May.
Schär, Fabian (2021). Decentralized Finance: On Blockchain- and Smart Contract-Based Financial Markets, in: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review, Second Quarter.
Institute of International Finance (2022). Russia: Crypto Assets and Sanctions Avoidance, Macro Notes, June 1.
CFTC (2021). CFTC Orders Tether and Bitfinex to Pay Fines Totaling $42.5 Million, Release Number 8450-21, October 15.
European Commission (2020). Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on Markets in Crypto-assets, and amending Directive (EU) 2019/1937, September 24.
President’s Working Group on Financial Markets, FDIC and OCC (2021). Report on Stablecoins, November.
See for example Die Deutsche Kreditwirtschaft (2021). Europe needs new money – an ecosystem of CBDC, tokenised commercial bank money and trigger solutions, July 5.
See https://cbdctracker.org for an overview of current CBDC projects.