

This policy brief is based on Deutsche Bundesbank Discussion Paper No 12/2025. The views expressed in this brief are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Deutsche Bundesbank or the Eurosystem.
Abstract
Central banks have used communication about the inflation outlook as an additional policy tool in response to the post-pandemic inflation surge. We present novel survey evidence that the ECB’s guidance about its projected inflation path can substantially lower households’ inflation expectations when kept in a sophisticatedly simple (KISS) way.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and the onset of Russia’s war against Ukraine, central banks worldwide have struggled to contain inflation. When inflation rates run substantially above the central bank’s inflation target over a prolonged period, inflation expectations risk de-anchoring. This could impede the price and wage formation processes in the economy and have undesirable effects on price stability. To inform economic agents, central banks have increasingly used communication about their inflation outlook to limit spillover from realized to expected inflation.
We fielded two experiments with around 10,000 participants in the Bundesbank Online Panel Households (BOP-HH) in March and October 2022, a time when inflation rates were sharply rising. We provided participants with samples of numerical, verbal, and visual ECB communication about the inflation outlook and assessed which type of central bank communication is most effective in guiding inflation expectations toward the ECB’s two percent inflation target. We observe that “words speak louder than numbers”. People seem to better understand a qualitative, verbal explanation than a numerical presentation of the inflation outlook. Moreover, “a picture seems worth a thousand words”, since households align their expectations most strongly to a streamlined illustration of the projected course of inflation. Based on these findings, we suggest that central banks should keep it sophisticatedly simple (KISS) when communicating with the general public.
We randomly assigned survey participants to several subgroups in the survey. Each of these groups received a different type of ECB communication regarding the latest inflation outlook in the form of small texts, newspaper interview excerpts or parts of speeches. For example, one group received a text containing the projected rate of inflation for the next years in the form of actual numbers. Another group received an excerpt from a newspaper interview in which an ECB official explains the expected inflation path in a qualitative manner only. In the October survey wave, some participants were also provided with a graph representing the ECB’s latest inflation projections. There was always a group of survey respondents, the control group, which did not receive any additional central bank communication.
After the participants were provided with their respective information pieces, we surveyed all groups including the control group to collect their short, medium and longer-term inflation expectations for comparison of these assessments.
Overall, we find that central bank communication works well in steering households’ expected inflation towards the target.
In Figure 1, the black horizontal line shows the average inflation rates expected by private households in the control group in March 2022. In Figure 2, the black line shows those expected inflation rates in October 2022. The blue and red bars represent the reduction in expected inflation through central bank communication.
From both figures, it can be concluded that informing private households about the inflation outlook can lead households to adjust their expected inflation rates for the short (left graph), medium (middle graph) and longer (right graph) term towards the inflation target. For both survey periods, however, we can find different degrees of effectiveness of the various forms of communication.
Figure 1. Selected treatment effects Bundesbank Online Panel Households (BOP-HH) March 2022
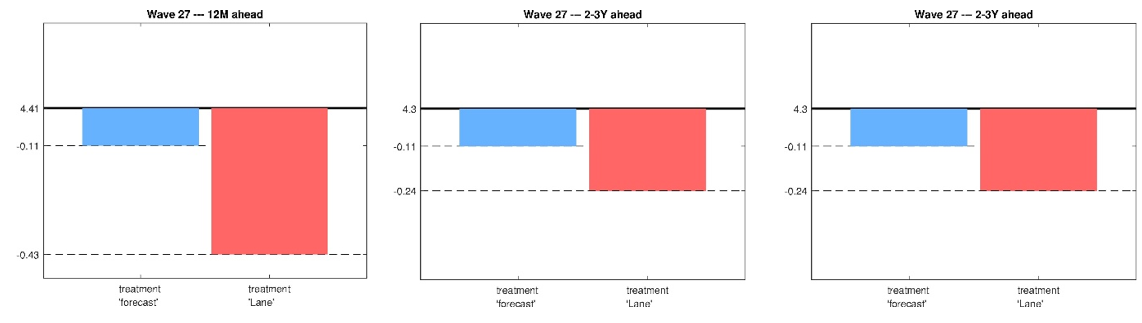
Notes: The left graph shows information effects for expected inflation twelve months ahead, the middle graph for expected inflation two to three years ahead, the right graph for five to ten years ahead. The black horizontal line corresponds to the mean expected inflation of the control group. The blue bar shows the reduction in the group that received a text with the inflation data projected by the ECB for the next three years in form of actual numbers. The red bar shows the reduction in the group that received a text with a press interview in which ECB chief economist Philipp Lane explains the inflation projections in a qualitative way.
In March 2022, the euro area faced a novel situation where inflation rates continued rising to levels far above the ECB’s inflation target of 2%. We observe that communicating the outlook in numerical terms (i.e. the blue bar of Figure 1) shows only a minor response of expected inflation. Yet, describing the outlook in a verbal, qualitative and non-technical manner using positively framed language significantly reduces households’ inflation expectations (see the red bar of Figure 1). We therefore conclude that during this period “words speak louder than numbers”.
By October 2022, households had experienced rising rates for some time, peaking above 10%. We observe again that positively framed, reassuring communication without any numerical detail (i.e. blue bar of Figure 2) substantially reduces inflation expectations, in particular for the short term. Yet, we find that displaying the projected return of inflation back to the target level in a simple visual representation seems to convey the key message even more effectively for farther horizons. Households’ expected inflation is lowered significantly, even at longer expectation horizons (see the red bars of Figure 2). Hence, a graph seems to be at least as effective as a press statement. These findings lead us to agree that “a picture is worth a thousand words”.
Figure 2. Selected treatment effects Bundesbank Online Panel Households (BOP-HH) October 2022
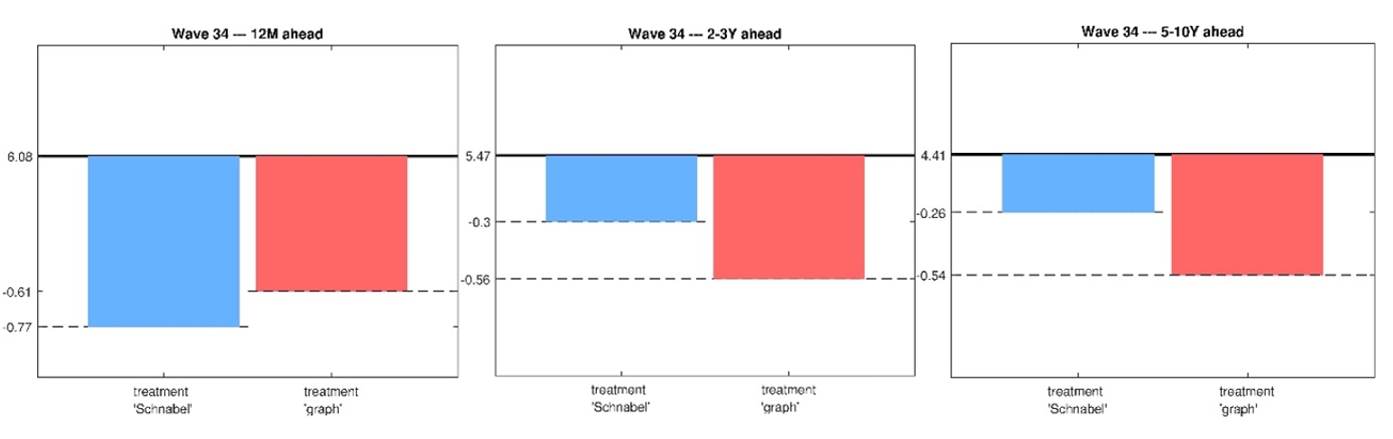
Notes: The left graph shows information effects for expected inflation twelve months in advance, the middle graph for expected inflation two to three years in advance, the right graph for five to ten years in advance. The black horizontal line corresponds to the mean expected inflation of the control group. The blue bar shows the reduction in the group that received a text with excerpts from a speech in which ECB Council member Isabel Schnabel speaks qualitatively about the inflation outlook. The red bar shows the reduction in the group that received a graph showing the projected inflation figures visually.
We provide novel survey evidence that certain forms of communication achieve higher reductions in elevated expected inflation rates than others. We concur with the proverbs “words speak louder than numbers” and “a picture is worth a thousand words”. If central bank communication aims at maximising its outreach to a broad and diverse audience, easy-to-process graphs and positively framed non-technical and relatable verbal explanations emerge as effective vehicles to do so. Further experiments varying only marginal details in such communication appear useful to clearly separate the influences of single factors. In any case, to successfully address the entire cross-sectional distribution of information recipients, we suggest that central banks should follow the “KISS” principle and keep it sophisticatedly simple.
Hoffmann, M., Mönch, E., Pavlova, L. and Schultefrankenfeld, G. (2023), „A KISS for central bank communication in times of high inflation“, Bundesbank Discussion Paper 12/2025